Filecoin - PoREP电路介绍
PoREP电路相关的逻辑在storage-proofs/src/porep/stacked/circuit/目录中。Rust-fil-proofs代码更新比较快,本文中用的代码的最后一个commit信息如下:
commit 14870d715f1f6019aba3f72772659e38184378bf Author: Rod Vagg Date: Fri Mar 20 22:30:18 2020 +1100 feat(filecoin-proofs): expose filecoin_proofs::pad_reader
只要SDR算法不变,大致的电路逻辑不会有大的变化。对SDR算法不熟悉对小伙伴,可以看看:
Filecoin - 为什么SDR这么慢?
整个PoREP电路的代码框架如下图所示:
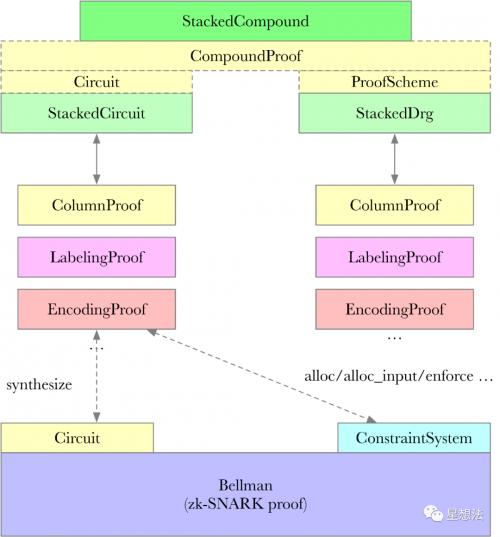
从StackedCircuit讲起。
StackedCircuit就是PoREP的整体电路。StackedCircuit定义在storage-proofs/src/porep/stacked/circuit/proof.rs中。
pub struct StackedCircuit<'a, e:="" h:="" static="" g:="" hasher=""> {
params: &'a E::Params,
public_params:<StackedDrg<'a, g="">as ProofScheme<'a>>::PublicParams,
replica_id: Option
comm_d: Option
comm_r: Option
comm_r_last: Option
comm_c: Option
proofs: Vec<Proof
}其中
params - JubjubEngine的相关参数,
public_params - StackedDrg(深度鲁棒图)相关的参数,包括图本身的参数以及挑战的个数。
replica_id - Sector复制id
comm_d - 原始数据的二叉树的树根
comm_r - comm_r_last和comm_c的hash结果
comm_r_last - encoding之后的数据的八叉树的树根
comm_c - column hash结果的八叉树的树根
proofs - 挑战对应的证明电路
整个电路的搭建,从StackedCircuit的synthesize接口函数开始。
impl<'a, h:="" g:="" hasher=""> Circuit fn synthesize<CS: ConstraintSystem
整个synthesize函数,将电路分割成两部分:1/ 树根校验电路 2/ 挑战的节点信息证明电路。其中树根校验电路比较简单易懂。申请replica_id_bits, comm_d,comm_r,comm_r_last以及comm_c变量,并验证comm_c和comm_r_last是否可以正确计算出comm_r。
Sector大小为32G的情况下,挑战个数为144个。也就是说,整个挑战节点证明电路由144个小电路组成。
for (i, proof) in proofs.into_iter().enumerate() {
proof.synthesize(
&mut cs.namespace(|| format!("challenge_{}", i)),
&self.params,
public_params.layer_challenges.layers(),
&comm_d_num,
&comm_c_num,
&comm_r_last_num,
&replica_id_bits,
)?;
}每个挑战节点的小电路,由Proof结构表示(storage-proofs/src/porep/stacked/circuit/params.rs)。
pub struct Proof pub comm_d_proof: InclusionPath pub comm_r_last_proof: InclusionPath pub replica_column_proof: ReplicaColumnProof pub labeling_proofs: Vec<(usize,>, pub encoding_proof: EncodingProof, }
Proof的结构比较清晰,分别包括了:
comm_d_proof - 原始数据的Merkle树证明
encoding_proof - Encoding的结果证明
comm_r_last_proof - Encoding结果的Merkle树证明
labeling_proofs - Labeling计算证明
replica_column_proof - column hash的计算证明
Proof的synthesize函数构建如上的证明。
原始数据的Merkle树证明电路证明comm_d_leaf的节点,在以comm_d为树根的Merkle树上。
let comm_d_leaf = comm_d_proof.alloc_value(cs.namespace(|| "comm_d_leaf"))?; comm_d_proof.synthesize( cs.namespace(|| "comm_d_inclusion"), params, comm_d.clone(), comm_d_leaf.clone(), )?;
其中comm_d_leaf是电路中的变量。comm_d_proof是InclusionPath结构,定义在storage-proofs/src/porep/stacked/circuit/params.rs中。InclusionPath电路的核心逻辑在synthesize函数中:
pub fn synthesize<CS: ConstraintSystem
self,
cs: CS,
params: &
root: num::AllocatedNum
leaf: num::AllocatedNum
) -> Result<(), synthesiserror=""> {
let InclusionPath { auth_path, .. } = self;
let root = Root::from_allocated::
let value = Root::from_allocated::
PoRCircuit::
}可以发现,所有证明Retrieval的电路,都是通过PoRCircuit实现。也就是说,目前的PoR是通过Merkle树实现的。PoRCircuit电路定义在storage-proofs/src/gadgets/por.rs。PoRCircuit的电路就是结合叶子节点和路径信息,查看最后“计算”出来的树根和提供的树根是否一致。具体相关逻辑,小伙伴可以自行查看。
Labeling计算的证明电路就是证明某个节点按照SDR算法正确计算。
for (layer, proof) in labeling_proofs.into_iter() {
let raw = replica_column_proof.c_x.get_node_at_layer(layer);
let labeled_node =
num::AllocatedNum::alloc(cs.namespace(|| format!("label_node_{}", layer)), || {
raw.map(Into::into)
.ok_or_else(|| SynthesisError::AssignmentMissing)
})?;
proof.synthesize(
cs.namespace(|| format!("labeling_proof_{}", layer)),
params,
replica_id,
&labeled_node,
)?;
}在某一层上的某个节点的Labeling的结果数据通过replica_column_proof.c_x.get_node_at_layer(layer)可以获取。Labeling的计算电路由LabelingProof结构的synthesize函数实现:
pub fn synthesize<CS: ConstraintSystem
self,
mut cs: CS,
params: &
replica_id: &[Boolean],
exp_encoded_node: &num::AllocatedNum
) -> Result<(), synthesiserror=""> {
let LabelingProof { node, parents } = self;
let key = Self::create_label(
cs.namespace(|| "create_label"),
params,
replica_id,
node,
parents,
)?;
// enforce equality
constraint::equal(&mut cs, || "equality_key", &exp_encoded_node, &key);
Ok(())
}
}其中的create_label函数又是由两个电路构成:create_label_circuit和sha256_circuit。也就是说,这两个电路就是把依赖的(parents)的节点数据进行sha256计算。constraint::equal就是来确认“计算”出的节点数据和提供的节点数据是否一致。
Encoding计算就是将最后一层的节点数据和原始数据进行Encoding。Encoding的计算方式就是大数加法,具体的计算storage-proofs/src/gadgets/encode.rs文件中。
encoding_proof.synthesize(
cs.namespace(|| format!("encoding_proof_{}", layers)),
params,
replica_id,
&comm_r_last_data_leaf,
&comm_d_leaf,
)?;整个Encoding证明电路由EncodingProof的synthesize函数实现。简单的说,Encoding的电路验证过程首先计算Labeling,然后对comm_d_leaf进行Encoding计算,判断结果是否和comm_r_last_data_leaf一致。
类似于原始数据的Merkle树证明电路证明,证明comm_r_last_data_leaf在comm_r_last的Merkle树上。只是这棵树是八叉树。
comm_r_last_proof.synthesize( cs.namespace(|| "comm_r_last_data_inclusion"), params, comm_r_last.clone(), comm_r_last_data_leaf, )?;
Column hash的证明电路是由ReplicaColumnProof结构的synthesize实现,具体定义在storage-proofs/src/porep/stacked/circuit/params.rs中。
replica_column_proof.synthesize(cs.namespace(|| "replica_column_proof"), params, comm_c)?;
大致的逻辑是,先处理挑战节点的Column信息,再分别处理base和exp依赖节点的Column信息:
// c_x
c_x.synthesize(cs.namespace(|| "c_x"), params, comm_c)?;
// drg parents
for (i, parent) in drg_parents.into_iter().enumerate() {
parent.synthesize(cs.namespace(|| format!("drg_parent_{}", i)), params, comm_c)?;
}
// exp parents
for (i, parent) in exp_parents.into_iter().enumerate() {
parent.synthesize(cs.namespace(|| format!("exp_parent_{}", i)), params, comm_c)?;
}也就是说,证明电路由15个ColumnProof子电路组成。ColumnProof定义在storage-proofs/src/porep/stacked/circuit/column_proof.rs中。
pub struct ColumnProof column: Column, inclusion_path: InclusionPath }
相应的电路生成逻辑在ColumnProof的synthesize函数中:
let c_i = column.hash(cs.namespace(|| "column_hash"), params)?; let leaf_num = inclusion_path.alloc_value(cs.namespace(|| "leaf"))?; constraint::equal(&mut cs, || "enforce column_hash = leaf", &c_i, &leaf_num); // TODO: currently allocating the leaf twice, inclusion path should take the already allocated leaf. inclusion_path.synthesize( cs.namespace(|| "column_proof_all_inclusion"), params, comm_c.clone(), leaf_num, )?;
column.hash计算出Column对应的hash结果。检查这个结果是否与leaf_num相等。同时查看这个leaf_num是否在comm_c的Merkle树上。
到目前为止,整个电路的全貌已经出现:
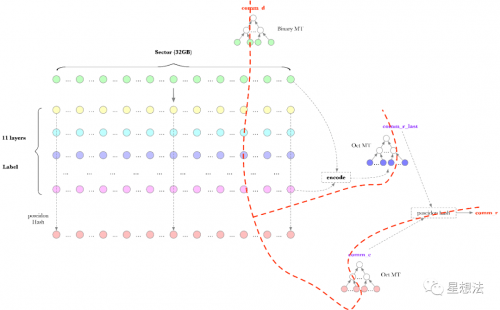
整个PoREP的电路的公开输入由StackedCompound的generate_public_inputs函数实现,具体实现在storage-proofs/src/porep/stacked/circuit/proof.rs文件中。
fn generate_public_inputs( pub_in: &<StackedDrg pub_params: &<StackedDrg k: Option ) -> Result<Vec
其中k为parition的编号。对于32G的Sector,总共有9个Paritition。
comm_d & comm_r
let comm_d = pub_in.tau.as_ref().expect("missing tau").comm_d;
let comm_r = pub_in.tau.as_ref().expect("missing tau").comm_r;挑战对应comm_d的存在性证明
目前PoRCompound,只把Merkle树的路径信息作为公开输入。
inputs.extend(PoRCompound:: &pub_inputs, &por_params, k, )?);
挑战对应的一系列comm_c的存在性证明
注意,comm_d的计算是二叉树,comm_c的计算是八叉树。
// c_x
inputs.extend(generate_inclusion_inputs(challenge)?);
// drg parents
let mut drg_parents = vec![0; graph.base_graph().degree()];
graph.base_graph().parents(challenge, &mut drg_parents)?;
for parent in drg_parents.into_iter() {
inputs.extend(generate_inclusion_inputs(parent as usize)?);
}
// exp parents
let mut exp_parents = vec![0; graph.expansion_degree()];
graph.expanded_parents(challenge, &mut exp_parents);
for parent in exp_parents.into_iter() {
inputs.extend(generate_inclusion_inputs(parent as usize)?);
}挑战对应的comm_r_last的存在性证明
inputs.extend(generate_inclusion_inputs(challenge)?);
总结:
PoREP的电路验证了Sector的计算过程,从Labeling,Encoding到Column Hash。注意的是,在Sector大小为32G的情况下,电路包括144个挑战节点的计算。电路相应的公开输入除了comm_d和comm_r外,还有各个Merkle树的路径信息。
声明:此文出于传递更多信息之目的,并不意味着赞同其观点或证实其描述。本网站所提供的信息,只供参考之用。







